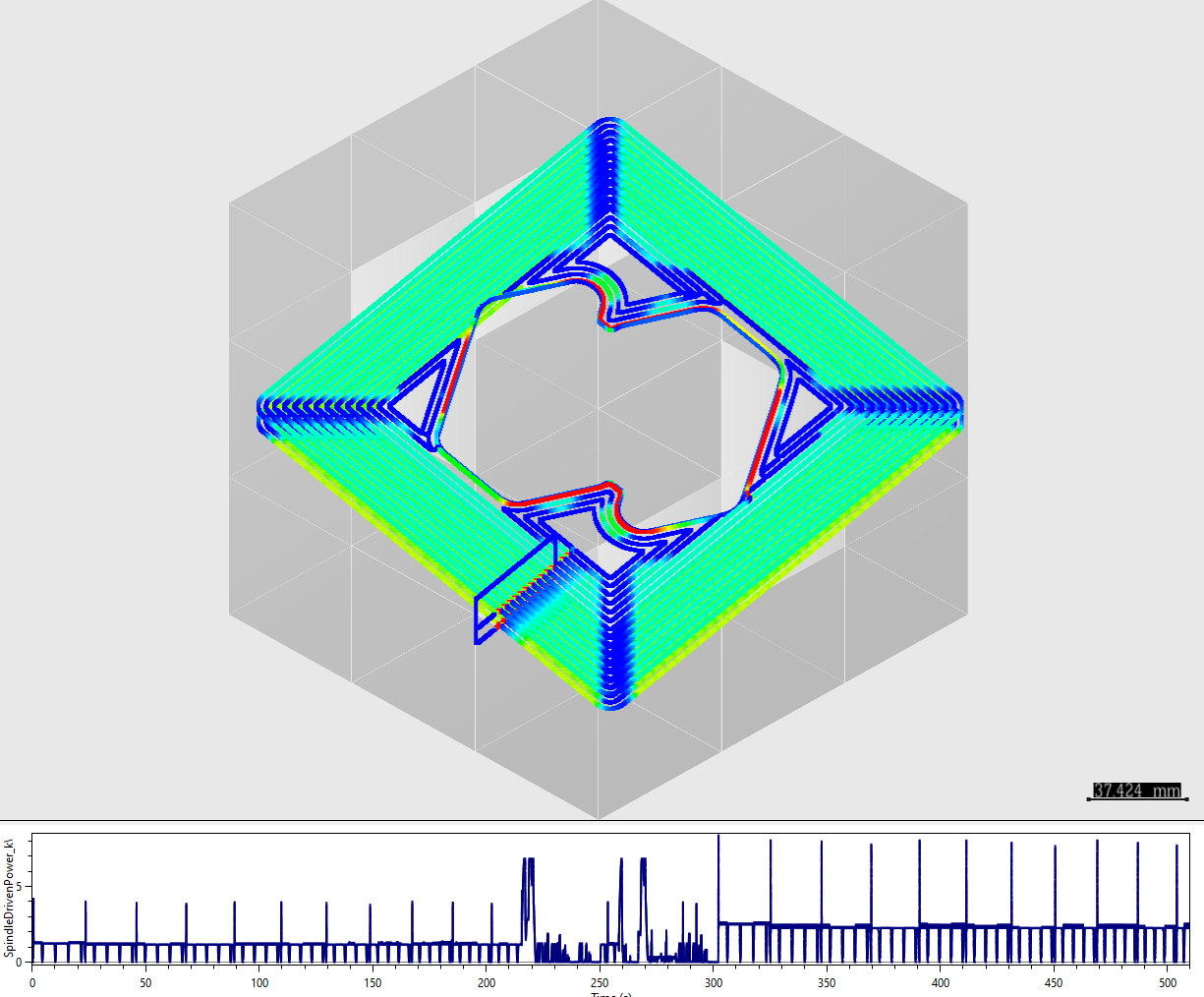
Spindle Power Evaluation
The role of spindle power for energy cost of Milling
The distribution scheme is shown by Heidenhain's document:
Quotes from Heidenhain, Technical Information Aspects of Energy Efficiency in Machine Tools, November 2010.
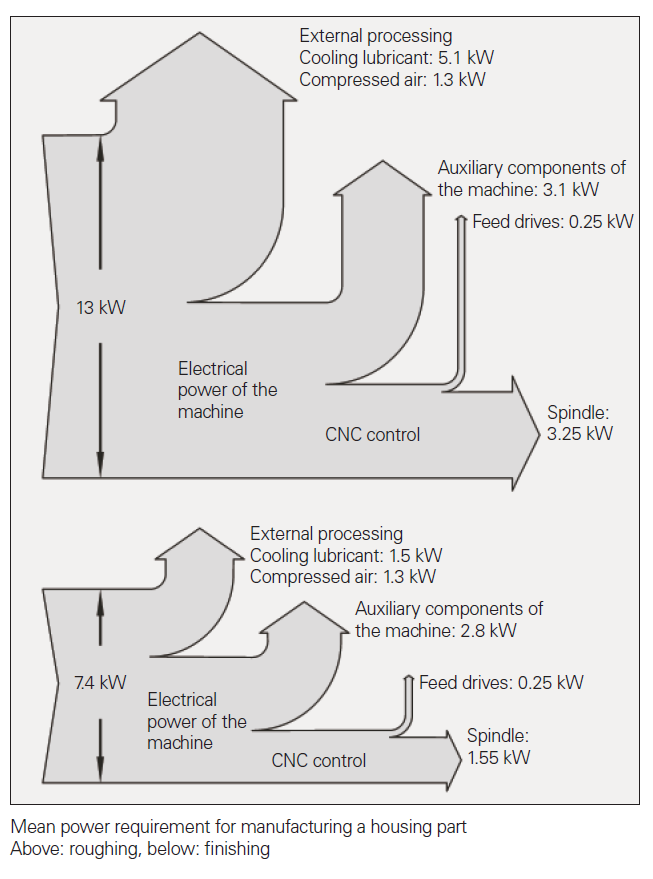
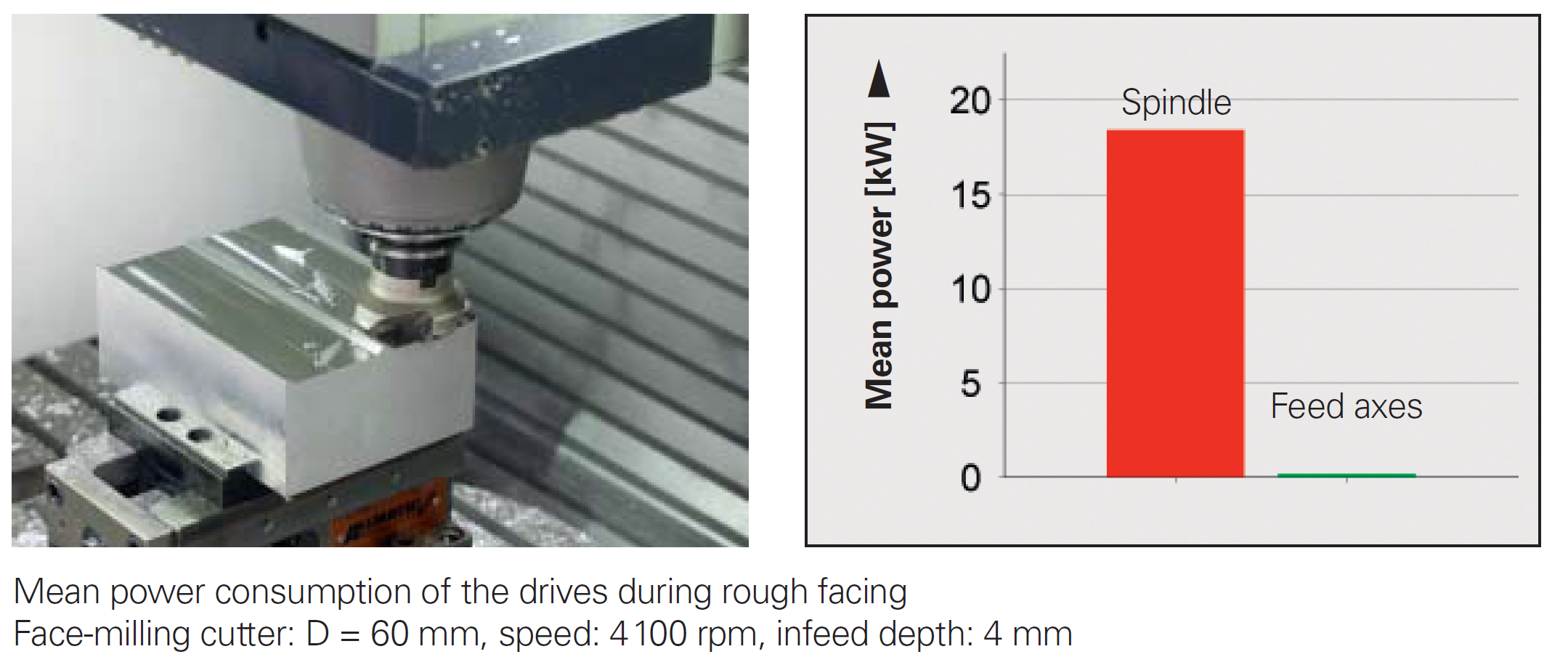
In the quoted example, the workpiece material seems like Al6061. Feed axis motors & main spindle cost about 27% of the total power.
From HiNC spindle power evaluation:
- Milling S45C cost 200% energy compare to Al6061T6.
- Milling Inconel718 cost 800% energy compare to Al6061T6
i.e.,
- Spindle power of milling S45C occupies 42% of total power.
- Spindle power of milling Inconel718 occupies 75% of total power.
Conclusion: Spindle Power matters for not easy-working materials for computing the energy cost of milling.
Verification of HiNC Spindle Power Evaluation
HiNC Spindle Power Evaluation is verified by comparison of the gathering Data based on the following setting.
Setting
- Machine Tool: YCM NDV102A
- Max Spindle Power: 22.4 kW
- Controller: Fanuc 31i-Model A
- Sampling: 1ms
-
Total Spindle Expended Energy: 0.412 kWh
The total spindle expended energy is rearranged from Fanuc ServoGuide TCMD data.
-
Work Time: 8min 30s
Comparison
The following figures are spindle power based on Controller and the spindle power evaluated by HiNC.
The spindle power by Fanuc ServoGuide TCMD(%) * MaxSpindlePower
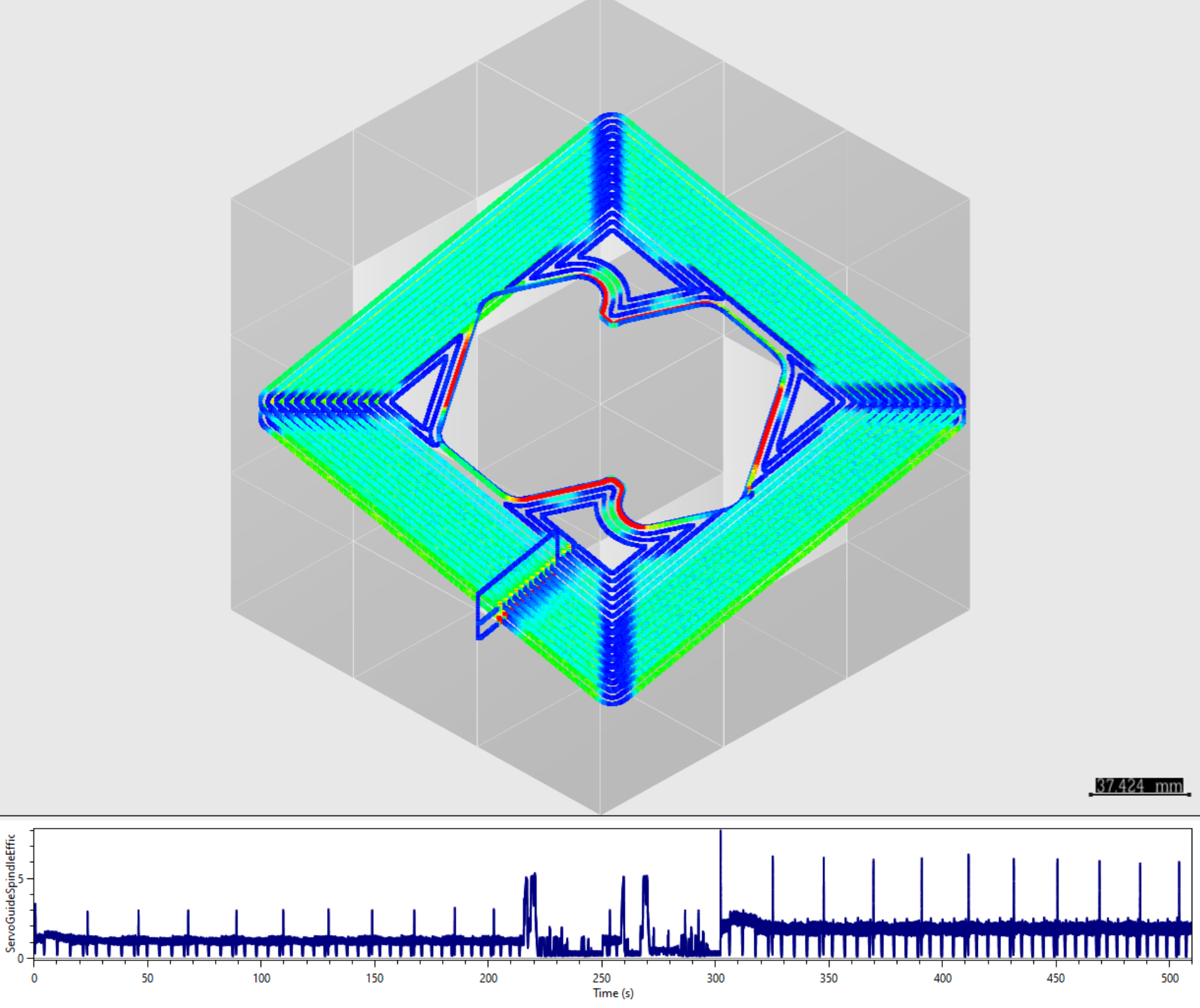
The evaluated sindle power by HiNC Milling Power * Energy Conversion Efficiency (here is 0.4)